Welcome, Caravelers! In this post, we are going to take a journey into the world of linguistics. As we all know, learning a new language can be both thrilling and intimidating at the same time. While some of us aim to master the language fluently, others find themselves drawn to the intricate details of language rules and the subtle nuances of meaning. These individuals yearn for more than just a surface-level understanding of the words spoken by others. And that's where linguistics comes in. It is the key to unlock the deeper layers of a language, starting with its basic structure and leading to a comprehensive understanding of its true essence. So let's embark on this exciting journey together and explore the mysteries of language through the lens of linguistics!
What is Linguistics?
Consider the profession of a lawyer. Although language is undoubtedly a tool for communication, being a successful lawyer requires more than just fluency in a language. Lawyers must be skilled at analyzing language in various forms, including spoken, written, and other contexts. This specialized field is known as linguistics.
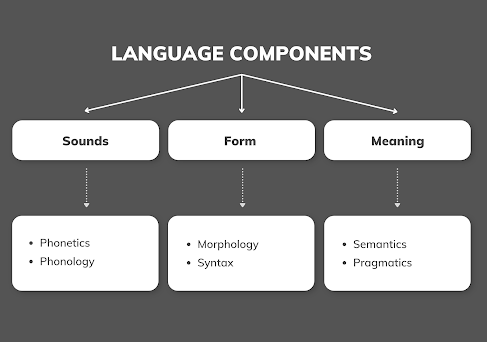
According to The American Heritage Dictionary, linguistics is the study of language and its structure, which encompasses sounds, form, and meaning. Its aim is to gain a deeper understanding of how humans acquire, process, and use language, as well as how language varies across different contexts. Think of it as being a detective investigating how people talk and write. We scrutinize every sound we make, every word we use, and even the ways in which languages change over time.
Learning a language in school is one thing, but studying linguistics takes it to a whole new level. It delves deep into the intricate details of language and provides a broader understanding of its complexities, beyond simple present, past, or future tenses.
Language Components
Now, we know that linguistics is the term used to describe the various fields of study that are involved in understanding and analyzing language. From phonetics to semantics, all these components come together to make language what it is. When we engage in conversation, we are using these language components without even realizing it. But have you ever wondered what would happen if we had a deeper understanding of each component? The more knowledge we have about each aspect of language, the more we can investigate how we use it. This investigation can help us to communicate more effectively, to express our thoughts and emotions more accurately, and to connect with others on a deeper level. So next time you are having a conversation, take a moment to consider the intricacies of the language you are using, and appreciate this field of study. To get started, let's take a closer look at each language component, including syntax, phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. By building a solid foundation of knowledge, you will be well-equipped to explore this subject further in future posts.
1. Phonetics
The field of phonetics comes into play when we try to understand how we are able to produce the wide variety of sounds that make up human speech. According to Fairbanks (1954), phonetics is the branch of linguistics that deals with the physical aspects of speech production. Essentially, it is the study of how we make sounds when we talk. This biological action involves a complex interplay between our lungs, vocal cords, tongue, lips, and other parts of our body. The sounds we make during this process are known as speech sounds, and when strung together in a particular order, they form words and sentences. By studying the way different speech sounds are produced and how they are represented in writing, we can learn to pronounce words like "plate" correctly. For example, the phonetic transcription of "plate" is [p] [l] [e] [ɪ] [t], which tells us which parts of the mouth each sound comes from. So, whether you're a linguistics enthusiast or just curious about the mechanics of speech, phonetics provides a glimpse into the inner workings of human language.
2. Phonology
If you're curious about how sounds are pronounced differently across languages, you might be interested in phonology, which is the next branch of linguistics.Phonology focuses on the way sounds vary across different languages, building on the foundation laid by phonetics. In this subject, we compare the pronunciation of sounds in one language to another to better understand the differences and similarities between them.
One example of this is the phoneme /r/. This sound can be pronounced differently in various languages, and each language has its own set of allophones for this phoneme. For instance, in English, it might be pronounced as [ɹ], while in German, it could be [R], and in Italian, it might be [ɾ].
It's not always easy to distinguish between phonetics and phonology, as they can seem quite similar. However, Phloneme (2012) offers an insightful metaphor to help clarify the difference between the two fields. Imagine a house with different doors. The phoneme /r/ is like the house, while the allophones learned in phonetics are like the doors. Depending on the language we are learning, the allophones for the phoneme /r/ may be different, just as different houses may have different doors. By exploring these differences and similarities, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex world of language.
3. Morphology
The next branch of linguistics is Morphology. It is a captivating subject that study the words in any languages and how they are created. When we examine each word that we use, we can discover a lot about its form. For instance, the word "happy" is a free morpheme because it can stand alone and convey meaning on its own. However, if we add a bound morpheme like "un" to it, the resulting word "unhappy" acquires a completely new meaning that is the opposite of the original word (CrashCourse, 2020). This is a common way of creating new words in language. By understanding how morphemes work and how they combine, we can enhance our vocabulary and communication skills in the language we are learning. As we go deeper into this subject, we will come across terms like suffixes and prefixes that add meaning to words, and we will learn how they can be used to create entirely new words.
4. Syntax
Have you ever wondered why we can understand complex sentences and express our thoughts and ideas effectively? Well, the answer lies in syntax, a fascinating branch of linguistics that deals with the rules governing the structure of sentences. In simple terms, syntax is like a recipe book for language. Just like a recipe book tells you how to combine different ingredients to create a delicious dish, syntax tells you how to organize and combine words, phrases, clauses, and sentences to create meaningful communication (West & Weber, 1974).
As we dive deeper into this subject, we will come across terms such as noun phrase, verb phrase, prepositional phrase, and sentence types. These terms help us understand the different building blocks of sentences and how they fit together to create meaning. For instance, let's take the sentence "When I saw her, I immediately went to bed". This sentence has two parts - "when I saw her" and "I immediately went to bed". The first part is a dependent clause, while the second part is an independent clause. The independent clause can stand alone and make complete sense, while the dependent clause cannot stand alone and needs an independent clause to complete its meaning.
So, syntax not only helps us understand how to create complex sentences, but it also helps us understand how to deconstruct them and analyze their meaning. It's truly amazing how much we can communicate with just a few basic building blocks, and syntax is one of subjects to be a successful language learner.
5. Semantics
Semantics is the study of meaning. Have you ever considered the meaning of a word like "cool?" Well, sometimes we use it to describe something awesome, while at other times, we use it to describe temperature. And if you ever find yourself unsure of a word's meaning, don't worry - lexicographers are people who specialize in creating and defining words in the dictionary.
While syntax focuses on the structure of sentences, semantics pays close attention to the meaning of words, phrases, sentences, and text in a language. This is why understanding the simple sentence, for example, "the cat talks" becomes important. While that sentence is syntactically correct, it is semantically questionable because cats, unfortunately, cannot talk (as far as we know!).
The importance of semantics is not limited to linguistics. It is also a crucial concept in programming languages, where specific words and phrases have designated meanings. For example, the heading codes <H1> and <H2> in web programming may seem interchangeable, but in fact, <H1> is used to indicate a heading that is more important than <H2>. Understanding the semantics of these codes is essential to creating a well-structured website (Lent, 2016). In short, semantics plays a vital role in our understanding of language and communication. By paying attention to the meaning of words, we can better understand how language works and how to use it effectively in various contexts.
6. Pragmatics
Pragmatics is an intriguing field of linguistics that explores the nuances of language and meaning. It focuses on how the context in which words are used can completely change their significance. Essentially, pragmatics seeks to uncover the practical implications of language use rather than simply studying theoretical aspects. For example, the phrase "sebuah botol air kosong" in Malaysia would typically mean a bottle of mineral water, but in Indonesia, it takes on an entirely different meaning: an empty bottle. This demonstrates how the same phrase can have drastically different meanings depending on the context.
Another interesting concept in pragmatics is "implicature" (CrashCourse, 2020). Consider the scenario where you ask someone for their phone number. If they don't understand the underlying implication that you are interested in them romantically, they may respond with the cheeky reply of "I don't know, can you?" However, if they do pick up on the subtext, they would respond differently. This highlights how much of our communication relies on indirect language and contextual cues.
Aside from that, artificial intelligence also continues to advance. It is exciting to see how it will develop. However, it's also worth noting that language is a complex and nuanced field, and AI may not be able to fully grasp the intricacies of pragmatics due to the many factors that contribute to meaning.
This is Where a "Discourse" Comes in!
Once we have learned the basic subjects in linguistics, we come across another crucial aspect of human communication called discourse. Essentially, discourse refers to any type of conversation or discussion that we engage in (Ehrlich & Romaniuk, 2013). Whether we are trying to persuade someone to buy a product from us, sharing information, or narrating a story, all these types of communication fall under the umbrella of discourse. They can occur in different settings, from formal to informal, such as in a classroom or while camping with friends around the lake.
Discourse involves exchanging a variety of ideas or messages through various modes of communication, such as visual, written, spoken, spatial, tactile, gestural, and aural. When we engage in discourse, we identify different elements, including the participants involved, the topics being discussed, the context, genre, discourse markers, and text structure.
To illustrate, let's say we're having a conversation with friends about the existence of God. We might start with a discussion on the first assumption of whether God exists or not, and then question each other's reasons for believing one way or the other. During this discourse, we might use discourse markers like "Well, that makes sense though" or "I kind of disagree with you on this point." The text structure would be a back-and-forth communication where we all share our opinions and ideas about the topic.
Understanding discourse can help us develop better communication skills, be more conscious of discourses that can take place through different modes of communication, enhance our critical thinking abilities, increase cultural awareness, and improve our social interaction. Therefore, studying linguistics is a foundation for comprehending and engaging in various types of discourses.
Sociolinguistics
Imagine you've already learned a variety of subjects, but now you want to know how to use them in the real world. That's where sociolinguistics comes in! This particular subject explores how language is connected to society, examining how we use language in different social settings, how it varies among different groups, and how social factors like ethnicity, gender, age, and social class influence language use (Nosirova & Farhodova, 2022). Basically, it shows us that language is a powerful tool for social communication. For instance, political issues can impact the way people speak in border areas between two countries. Language can also signal our social identity and group membership.
To fully understand this complex relationship between language and society, sociolinguistics draws upon theories and methods from a variety of fields, including linguistic sociology, anthropology, and psychology. By studying sociolinguistics, we can improve our cultural awareness, professional development, research ideas, and communication skills. It's an exciting and rewarding subject that helps us navigate the intricate ways that language shapes our social lives!
References
American Heritage Dictionary. (n.d.). Linguistics. In The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Retrieved April 21, 2023, from https://www.ahdictionary.com/word/search.html?q=linguistics
CrashCourse. (2020). Morphology: Crash Course Linguistics #2 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=93sK4jTGrss&t=2s
CrashCourse. (2020). Pragmatics: Crash Course Linguistics #6 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MPwpk-YgvjQ
Ehrlich, S., & Romaniuk, T. (2013). Discourse analysis. In R. Podesva & S. Devyani (Eds.), Research methods in linguistics (pp. 466–499). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Fairbanks, G. (1954). Systematic research in experimental phonetics:* 1. A theory of the speech mechanism as a servosystem. Journal of speech and Hearing Disorders, 19(2), 133-139.
Lent, C. L. (2016). Introduction to HTML5. Retrieved from https://www.coursera.org/learn/html?
Nosirova, M. F., & Farhodova, S. U. Q. (2022). The study of sociolinguistics and the implication of social factors. Science and Education, 3(5), 2017-2020.
Phloneme. (2012). Explained: The relationship between phonetics and phonology [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=61xIUzoMTTk
West, J. J., & Weber, J. L. (1974). A linguistic analysis of the morphemic and syntactic structures of a hard-of-hearing child. Language and Speech, 17(1), 68-79.
















No comments:
Post a Comment